The effects of eight weeks handball exercises on social development in student of middle school in khorramshahr city
Download PDF
Valizadeh.R1, + , Zarghami.M 2, Baledi.R3, Hosseini.A.S 4, Feghhi.I5 1,5 Department of genral physical education, Omidiyeh Branch, Islamic Azad University , Omidiyeh, Iran 2Department of Sport Psychology, Shahid Chamran University , Ahvaz, Iran 3 Department of physical education, Abadan Branch, Islamic Azad University , Abadan, Iran 4 Department of physical education, Behbahan Branch, Islamic Azad University , Behbahan, Iran
The effects of eight weeks handball exercises on social development in student of middle school in khorramshahr city
Valizadeh.R1, + , Zarghami.M 2, Baledi.R3, Hosseini.A.S 4, Feghhi.I5
1,5 Department of genral physical education, Omidiyeh Branch, Islamic Azad University , Omidiyeh, Iran
2Department of Sport Psychology, Shahid Chamran University , Ahvaz, Iran
3 Department of physical education, Abadan Branch, Islamic Azad University , Abadan, Iran
4 Department of physical education, Behbahan Branch, Islamic Azad University , Behbahan, Iran
Social development is one of notable aspects of exist every person that not only affect to compatibility with suburbs but effect to range of educational success and advance In future. This aspects of development for example somatic or mental is a continues quantity and is perfected progressively. This is a semi experimental study that has been done by pretest & post-test design and control group. In this research the population of research was all men Student (n=7116),(age= 13-18) of middle school of khorramshar city in years of 2005-2006. The statistical sample in this study was 40 person, whom was selected by randomly method .that divided by experimental (n=20) and control (n=20) group. For evaluation of social development the (Weitzman.1981) questioner was used. The reliability of this questioner accepted by kronbakh alpha. At first statistical sample participated in pre-test and then divided by experimental and control group. Experimental groups for eight weeks, three sessions a week and each session for 90 minutes done handball exercises. Data analysis by computer using SPSS software and statistical methods of Descriptive and inferential (ANOVA &-test) was performed. Also the comparison, results of control and experimental groups showed that eight weeks handball exercises had significant changes on social development and all of aspects of experimental group, except hopefulness and optimism. (a ≥0/05)
Key words : handball, Autonomously, Responsibility, Relation and Compatibility, Hopefulness, Whole Social Growth
1. Introduction
Communication and how make relationship with together was the favorite case of the worlds men during the past and now. Man kind always made ready the way for affairs as the basis of life continuation and by this way man kind could gain their basic needs. In present century which is called communications century the value and importance of making relation with the world increased by means of a group life and making can yield important results against difficulties and also exploring the unidentified world. Its important to have true social development means growth of mans behavior in social relations as can be relevant and have a harmony with his society. A man is social when not only is beside others, but also cooperate with them [Aliakbar.1995].social growth is the indicator of those abilities that in connection with environment shows us the amount of learning. in the survey of social development, the purpose is indicate of that how much people can do daily activity of life and social communications[ Heshmatollah.1998]. Social development is another kind of growth that its recognition is more difficult than mental growth [Alice.1997].So it's more important for teenagers and young people who are at the beginning of progress and experience path. The importance of adolescence period is because of the growth of body forces and also due to expansion of mental potentials that arrives him to be a social and complete personality. Everything is changing in these years[2].So it should be expanded ,That is a man should be capable to obtain his independence, responsibility and communication with others as he needs that is gain an acceptable social growth. One of the ways to achieve social growth is sport exercise with it shows as a healthy way. Team sporting fields like handball can play an important role in social growth. Alinezhad says: body activity is on of principal elements of the children and teenagers. Body exercises is very effective for expanding of physical performances like motional skills and power of muscles and physiological potentials and energy production and working feed back and in other hard in children mental and social growth[Hamid.1997]. Mohammadi in a search by use of Witzmans social growth test and by compare individual athletes with team athletes and the non athletic students resulted that the team athletes in compare with two other groups have a greater social growth average [Reza.1999].Also vichel in an article under this title training of social skills by body training writes motion activities and sport. Has a great ability to grow positive social skills on students [Vigil.1996].And also based on deyvis and his colleae use in the book of psychology and sport, sport and body activity has social effectiveness [Davise et al. 2000].So researcher try to engage group team exercises to assess amount of social growth and any changes in the students. In one of sport fields like handball same as other group fields, favorite result occurs when the men in addition to have series of personal characters like responsibility, should profit from harmonic communications for group actions. So this research wants to study the effect of eight weeks handball exercises on social development (growth) of male students of intermediate course in khoramshahr, in a case that represents essential directions to teachers and parents and students.
2. Methods
The method of this research is semi experimental that studies the effect of eight week handball exercises on social development of male students of intermediate course khoramshahr bye use of pre-test research and post- test and control group.
2.1. Society and statistical sample.
Statistical society of this research consist of 7116 male students 13-18 year old in intermediate course in khoramshahr on education year 2005- 2006. In this research, sampling is done in randomly case, so khoramshahr town divided in five areas and then selected one school from each area in random case. Then divided 200 questionnaire randomly among the students of these five schools and so 40 persons who their grades were the least in social development (growth) at others ratio, were selected as the statistical sample.
2.2. Measurement tools.
From witzoman's social development questionnaire which consist of 27 questions is used for data collecting of this research. Some of the questions have 3 choices and others have 4 choices. This questionnaire shows the amount of social growth since 13 to 18 years old and has four dimensions which are: self-sufficiency (autonomy), responsibility acceptation, compatibility and communication with others and hopefully. witzman's social development is made by Ali's witzman. this questionnaire translated to persian by Sima Nazari[Noshabadi.2000].And Abassi has reported the final coefficient of the questionnaire 0/84 on the teenages 13 to 18 years old in tehran and esfahan cities[Heshmatollah.1998].For final study in this research , kronbakh's Alfa method was used which it's calculated amount is (r=0/81) in p<0/05 meaningful level. Also Abassi has reported the current coefficient of this questionnaire on the 13 to 18 years old teenagers in Tehran and Esfahan (r=0/75) which is on the level of p<0/05 meaningful [Heshmatollah.1998].There are 57 numbers in this questionnaire in all, which based on reply letter and with regard to person's choices, the grade of 0.1.2, 3 was given to the person in each question. Trainee select the best answer based on his idea, after the reading of the question and then marks it with(X).After the trainees answering, refer to answers key and the grades were given according to selective choice and the general grade calculates for him.
2.3. Statistical methods.
For data analysis, used from descriptive statistic (mean, standard deviation, tables, diagram…) and deduction statistic (variance analysis and t-test) which all the statistical operations were done by excel soft ware and SPSS® (version 11.5) with error (fault) modulus of a ≥0/05
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive part of research findings.
Table (1) shows the related data of descriptive statistic of general grades in social growth and its dimensions.
Table1: descriptive statistics of related grades to whole model in pretest
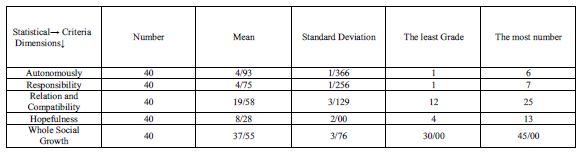
Also the random selection method is used to assign control and experimental group, which the related in formation of (data) to mean and standard deviation of the grades of social growth and it's dimensions for two experimental and control groups in the per-test said systematically in the tables(2,3)
Table2: Related grades to social development and its dimensions in experimental group in pre-test
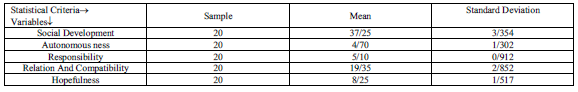
Table3: Related grades to social development and its dimensions in control group in pre-test
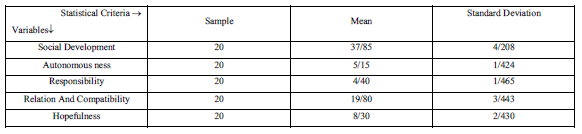
3.2. Deduction part of research findings.
In this section the use of deduction statistical methods show there is no meaningful difference between two experimental and control groups because of social growth and it's dimensions in pre-test on the level of a ≥0/05. Table4.The comparison of the variances of both two groups, shows, there is no meaningful difference between two groups in per-test.
Table4: F table (comparison of variances) in per-test
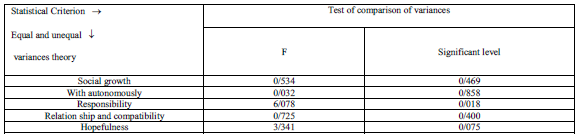
In the other hand, to ensure the results of table(4).For comparison of the means of two groups in social development and it's dimensions , T-test is used which the results in table (5).Shows there is no meaningful difference on the level of a ≥0/05 in per-test between two groups.
Table5: independent t-test, comparison between mean of two groups in pre-test
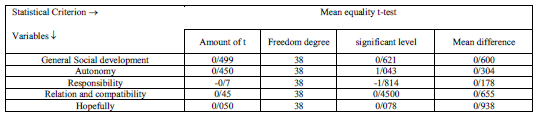
Since the results of tables four and five show that there is no significant difference between two groups in the level of a ≥0/05 in pre-test. So in this section, we compare post-test results in two experimental and control groups.
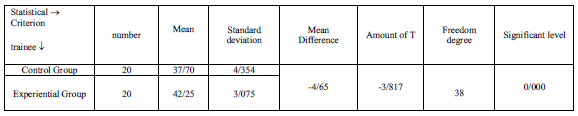
3.2.1. Table number(6).the results of independent t-test between two groups shows that there is significant difference between two groups in the meaningful level of p-value=0/000 . Also the results of this table shows well that the mean grades of experiential group are higher , in compare with control group. After 8 weeks handball exercises. So handball exercises have had a positive effect on the social development variable.
Table6: independent t-test for compare of social development of two groups in post-test
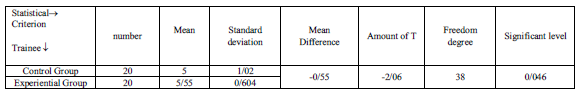
3.2.2. The data of table number (7).Show that there is significant difference between two groups in the meaningful level of p-value=0/046. Also being high the mean of autonomy in experimental group shows that handball exercises have had a positive effect on this variable.
Table7: independent t-test for comparison of autonomy of two groups in post-test
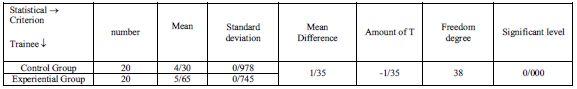
3.2.3. Also The data of table number (8).Shows that there is significant difference between two groups in the meaningful level of p-value=0/000. In other hand the comparison of the means shows influence of exercise on experimental group. So the results of this theory show that handball exercises could have positive influence on responsibility.
Table8: independent t-test for comparison of responsibility of two groups in post-test
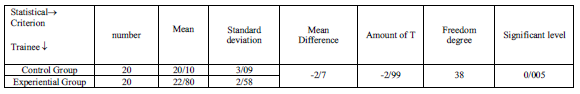
3.2.4. The data of table number(9) shows that there is significant difference between two groups on meaningful level of p-value=0/005.Also autonomy mean of experimental group shows handball exercises have a positive effect on compatibility and make relation.
Table9: independent t-test for comparison of compatibility and relation of two groups in post-test
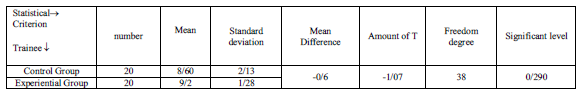
3.2.5. The data of table number (10) shows that there is no significant difference between two groups in the meaningful level of P-value=0/290.In fact this meaningful level shows that handball exercises have no influence on the dimension of hopefulness and optimism.
Table10: independent t-test for comparison of hopefulness and optimism of two groups in post-test
4. Discussion and conclusion
The findings of the research show that eight weeks handball exercises have influence on the sense of male students' autonomy. In other word, the students' autonomy who takes part in handball exercises was higher than others, meaningfully. It seems the completed researches have done more on social development from. and we cant find few researches which survey social development dimensions separately, so the results of this research in compare with stonsons research findings based upon sociality and autonomy by sport is weak or unremarkable a bout autonomy are disharmonious[Stevenson.1975].incompatibility of this finding with the findings of has done research ,may be for difference in place execution or the kind of sport field[Heshmatollah.1998].considering that the amount of obtained autonomy from participated students in handball group(team)athletes are good situations for developing the teenagers and youth autonomy level. Having the sense of autonomy in an acceptable extent has a good results on the individual life , in a way that person can take regarded decisions in the life with high self-confidence and access to his purpose just based on self-abilities and without depending on others. Having such men beside each other in a society cause a progressive society.
In this research, the comparison of the sense of responsibility in experimental group and control groups shows that there is a significant difference between the senses of responsibility in two groups after eight weeks handball exercise. It means responsibility among the students who took part in handball exercises in compare with others who did not participate in exercises is on higher level. in the researches, responsibility analyze as one of the dimensions of social development and hasn't studied separately. Any way the results of this variable are the same as many results of other researchers[Nico .2010].There from peoples responsibility is on of the development particulars in each society, we hope by people participating in grouped activities, more the society toward development.
The results of comparison compatibility and make relation with others between experimental and control groups after eight weeks showed that there is significant difference between two groups. In the other word compatibility and make relation with others among the students who participate in grouped handball exercises in compare with those who haven't participated are in a higher level. That these findings have harmony with other findings of researches[Daniel et al.2010., Marilyn .2009., Richard et al .2009., Laura et al.2009., Elizabeth et al 2009., Sam.2008., Gregory.2008., Philip et al.2007., Michael et al 2005., Michael et al .2000., ]
the results of comparison dimension of hopefulness and optimism between experimental and control groups after eight weeks showed that there is no significant difference between two groups. In the other word hopefulness and optimism of students that participate in handball exercise with those who didn't participate approximately was the same. These findings have no harmony with many other researches[Nico.2010.,Joseph et al.2007., Snyder et al .2006.,Suzanne et al.2006.,Cindy et al.2006]. Discordance of this finding with the finding of accomplished research, May be due to reasons like literacy level, culture and economy of statistical society of this research with other researches.
Also the results of comparison of the total social development in experimental and control group showed that there is a significant difference between the social developments of two groups after eight weeks handball exercise. It means the students who participated in handball exercise, in compare with those who didn't participate gregarious exercise, Have a higher social development, meaningfully. This finding has a harmony with findings of many other researchers[Fruchart et al.2010., David et al .2010., Michael et al.2006., Sarah et al.2009., Şenay et al.2009., Wylleman et al.2009., Gillet et al.2009., Mary et al.2009., Homas et al.2009., Eva.2009., James et al.2008., Athanasios et al.2008., Raphaël et al.2007., Julie et al.2007., Michel et al.2007 ]
Since the obtained amount related to students' social growth who participated in handball exercise is in a acceptable level, we can understand that handball as a gregarious sport. Brings development and higher students social growth. Having social developed people means to have men who can do their affairs independently and under take their responsibilities in different affairs and in this are compatible with another people, groups and institutions. Also can do healthy and beneficial relationship, combined with mutual respect. Such capability, allows the person that stable against in daily life problem and don't down against them.
5. Acknowledgments
Special thanks than all friends that help me about do this study and I wish they happiness.
6. References
[1] Aliakbar SH.N., The role of extracurricular activity in adolescent education .fifth edition. Etelaat publication .Tehran. 1995.
[2] Alice V., Social development (for youth and families). Translater by N.Sima, seventh edition, association of parents and coaches, Iran, 1997
[3] Athanasios G.P., George A., Periklis K., Alexandros S. Social agents, achievement goals, satisfaction and academic achievement in youth sport . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2008,9(2):122-141
[4] Cindy L. J., Kara B.W., Work Hope: Development and Initial Validation of a Measure . Journal of Counseling Psychology.2006, 53(1):94-106
[5] Daniel F.M., Mary A.H., Damon P.S. A., Stephen W.D., Organizational justice in sport . Sport Management Review.2010, 13(2):91-105
[6] David M., Vannessa J.T.. Need support and behavioural regulations for exercise among exercise referral scheme clients: The mediating role of psychological need satisfaction . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2010, 11(2):91-99
[7] Davise B., bull R., roscoe J., roscoe D., physical education and the study of sport. Indiana State University.2000
[8] Elizabeth R., Dawne L., Beth H., Barbara H., Helen P., Evidence for the validity of the Children's Attraction to Physical Activity questionnaire (CAPA) with young children . Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2009, 12(5):573-578
[9] Eva B., The effect of moderate exercise on growth and aggression depending on social rank in groups of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.) . Applied Animal Behaviour Science.2009, 119(1-2):115-119
[10] Fruchart E., Pâques P., Mullet E., and Decision-making in basketball and handball games: A developmental perspective . Revue Europeans de Psychologies Appliqué/European Review of Applied Psychology.2010, 60(1):27-34
[11] Gillet N., Berjot S., Paty B., Profile motivational et performance sportive . Psychologies Française.2009, 54(2):173-190
[12] Gregory C. J., George B.C., the Impact of Sport Management Students' Perceptions of Study Abroad Programs on Their Intentions to Study Abroad . Sport Management Review.2008, 11(2):149-163
[13] Hamid A.A.N., Effects of physical activity on children's growth. Second Congress of Sports Science with an emphasis on primary schools, first edition, physical education of education ministry,1997
[14] Heshmatollah A., Comparison of adolescents social development (13 to 16 years old), blind, semi-sighted vision and cities of Tehran and Isfahan. Psychology Masters thesis of Exceptional Children. College of Psychology and Educational Sciences. T.Allameh University .1998
[15] Homas D.R.T, Brian C.F., Donna S., Mediators of affective responses to acute exercise among women with high social physique anxiety . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2009, 10(5)573-578
[16] James S., Dwight H.Z., Jacqui C. Development through Sport: Building Social Capital in Disadvantaged Communities . Sport Management Review.2008, 11(3):253-275
[17] Joseph C., Patrick C.L., Fiona D.,
The impact of hope, self-esteem, and attribution style on adolescents' school grades and emotional well-being: A longitudinal study
. Journal of Research in Personality.2007, 41(6):1161-1178
[18] Julie C.S., Philippe G.S. Self-determination of contextual motivation, inter-context dynamics and adolescents' patterns of sport participation over time . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2007,8(5):685-703
[19] Laura B., Maurizio B., Claudio R., Dispositional goal orientations, motivational climate, and psychobiosocial states in youth sport . Personality and Individual Differences.2009, 47(1):18-24
[20] Marilyn L., The Peer Attitudes toward Children who stutter scale: Reliability, known group's validity, and negativity of elementary school-age children's attitudes . Journal of Fluency Disorders.2009, 34(2):72-86
[21] Michael S.W., Chih-Hung Ch., Terry D., Gregory M., Development and validation of the Communication and Attitudinal Self-Efficacy scale for cancer (CASE-cancer) . Patient Education and Counseling.2005, 57(3):333-341
[22] Michael J.F., David O., Eva L., Neville O., Interactive health communication in preventive medicine: Internet-based strategies in teaching and research . American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2000, 19(2):113-120
[23] Mary E. M., Michael G.P., the contributions of weight loss and increased physical fitness to improvements in health-related quality of life . Eating Behaviors.2009, 10(2):84-88
[24] Mary E. M., Michael G.P., the contributions of weight loss and increased physical fitness to improvements in health-related quality of life . Eating Behaviors.2009, 10(2):84-88
[25] Michael F.V., Scott Huebner E., Shannon M.S.. An analysis of hope as a psychological strength . Journal of School Psychology.2006,44(5):393-406
[26] Michel O., Serge H., Francis G., Serge B. Association between leisure-time physical activity and health-related quality of life changes over time . Preventive Medicine2007,44(3):202-208
[27] Nico S.., Roles and responsibilities of a change agent in sport event development projects . Sport Management Review.2010, 13(2):118-128
[28] Noshabadi S., Relationship between motor development and social growth of female students in athletic and non athletic area 6 of Tehran. MA thesis, Tehran University. college of Physical Education and Sport Science, 2000
[29] Philip J. S., Chris J.G., the Relationship between Athletic Satisfaction and Intateam Communication . Group Dynamics.2007,11(2):107-116
[30] Raphaël B., Jeffrey A.J., Ronald C.P. Physical activity level and health-related quality of life in the general adult population: A systematic review . Preventive Medicine.2007,45(6):401-415
[31] Reza M., Evaluation of social development fields of athletes participating in individual and team sports Olympiad fourth country boys schools (high school) in comparison with non-athlete students five areas of the esfahan city. Ministry of Education research project.1999
[32] Richard J. K., Chris G. H., Christopher M. S., David E. L., A qualitative investigation exploring the motivational climate in early career sports participants: Coach, parent and peer influences on sport motivation . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2009, 10(3):361-372
[33] Sam C., Adolescent-parent attachment characteristics and quality of youth sport friendship .Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2008,11(2):653-661
[34] Sarah U.F., Alan L. S., Social and motivational predictors of continued youth sport participation . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2009, 10(1):87-95
[35] Şenay K., Füsun Ö. Rüçhan Ö., Yalçın Ş., an investigation of social self-efficacy expectations and assertiveness in multi-program high school students . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.2009, 1(1):623-629
[36] Snyder C.R., Kenneth A. L., Ben K., Yngve M., Hope for Rehabilitation and Vice Versa . Rehabilitation Psychology.2006,51(2):89-112
[37] Stevenson C.L., Socialization effects of participation in sport: a critical review of the research. The Research Quarterly.1975, 46(3):287-301
[38] Suzanne J.P., Megan W.G., Joseph C.R., Hope, learning goals, and task performance . Personality and Individual Differences.2006, 40(6):1099-1109
[39] Vigil D., Teaching social skills through physical education .Teaching elementary physical education.1996, 7(4):20
[40] Wylleman P., Harwood C.G., Elbe A. M., Reints A., Caluwé D., A perspective on education and professional development in applied sport psychology . Psychology of Sport and Exercise.2009, 10(4):435-446
+ Corresponding author. Valizadeh. Roholla,Faculty of physical Education & Sport Science of Islamic Azad University, Omidieh Branch, Iran.Tel:0098-9169868067, E-mail address: valizadeh8328@gmail.com

















